Spring Pressure Calculator
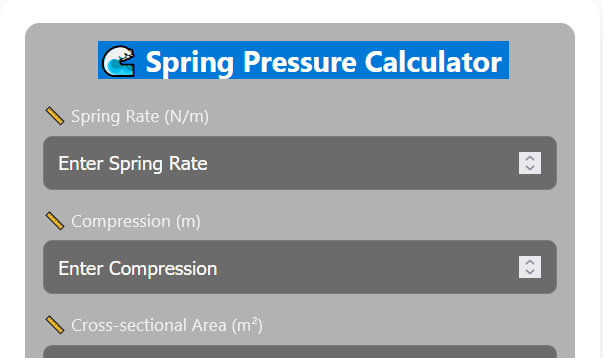
Spring pressure calculation helps mechanics and engineers quite a bit. It helps calculate the pressure of a spring to manage pressure distribution. Enter spring rate, compression, and cross-sectional area into the tool to calculate the required pressure.
Spring Pressure Calculator
Contents
Your result will be displayed here.
What Is Spring Pressure & How To Calculate
Spring pressure plays a key role in machines and industries. Springs help absorb shocks, transfer force, and support weight. Engineers use them to design car suspensions, factory machines, and precision tools.
Formula To Calculate Spring Pressure
When One Need To Calculation Pressure Of A Spring
For example, consider a car suspension that absorbs bumps on rough roads. The spring inside compresses under weight, creating pressure. If it exceeds 20,000 Pa, engineers adjust the spring’s stiffness or size to keep the suspension working properly and protect the car from damage.
Example Inputs:
- Spring Rate: 5000 N/m
- Compression: 0.02 m
- Cross-Sectional Area: 0.005 m²
✅ The calculated spring pressure is 20,000 Pa.
Pro Tip:
Shock springs are important for your vehicle’s suspension system. Check spring-loaded systems in vehicles regularly.
Key Insights (Pros & Cons)
Pros
-
Easy way to calculate accurate spring load pressure
-
Helps design safer and more responsive mechanical systems
-
Supports standard metric units for engineering accuracy
Cons
-
Doesn’t support imperial units (like lb/in)
-
Only valid for linear compression (no torsion or dynamic movement)
FAQs
1. What does this calculator do?
It calculates the pressure a spring applies based on its compression, spring rate, and area.
2. Why is spring pressure important?
It helps manage force distribution in mechanical systems like suspensions and machinery.
3. What inputs are needed?
Spring rate (N/m), compression distance (m), and cross-sectional area (m²).
4. Can this be used for automotive systems?
Yes, it’s commonly used for suspension analysis and tuning.
5. What’s the formula used?
Spring Pressure = (Spring Rate × Compression) ÷ Area
Calculation Summary
-
Spring Rate (K): Resistance level of the spring per unit compression
-
Compression (x): How much the spring is pressed
-
Cross-sectional Area (A): Surface area resisting the applied force
-
Formula: P = (K × x) ÷ A
-
Output: Resulting pressure in Pascals (Pa)
-
Application: Automotive shocks, industrial machines, precision tools