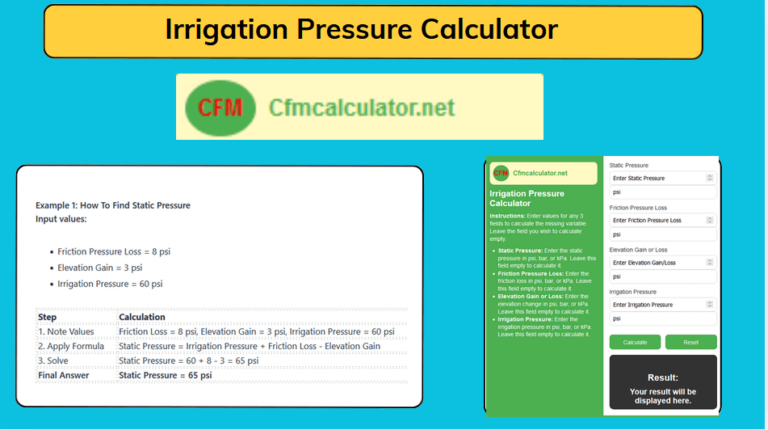
CFM to FPS Calculator
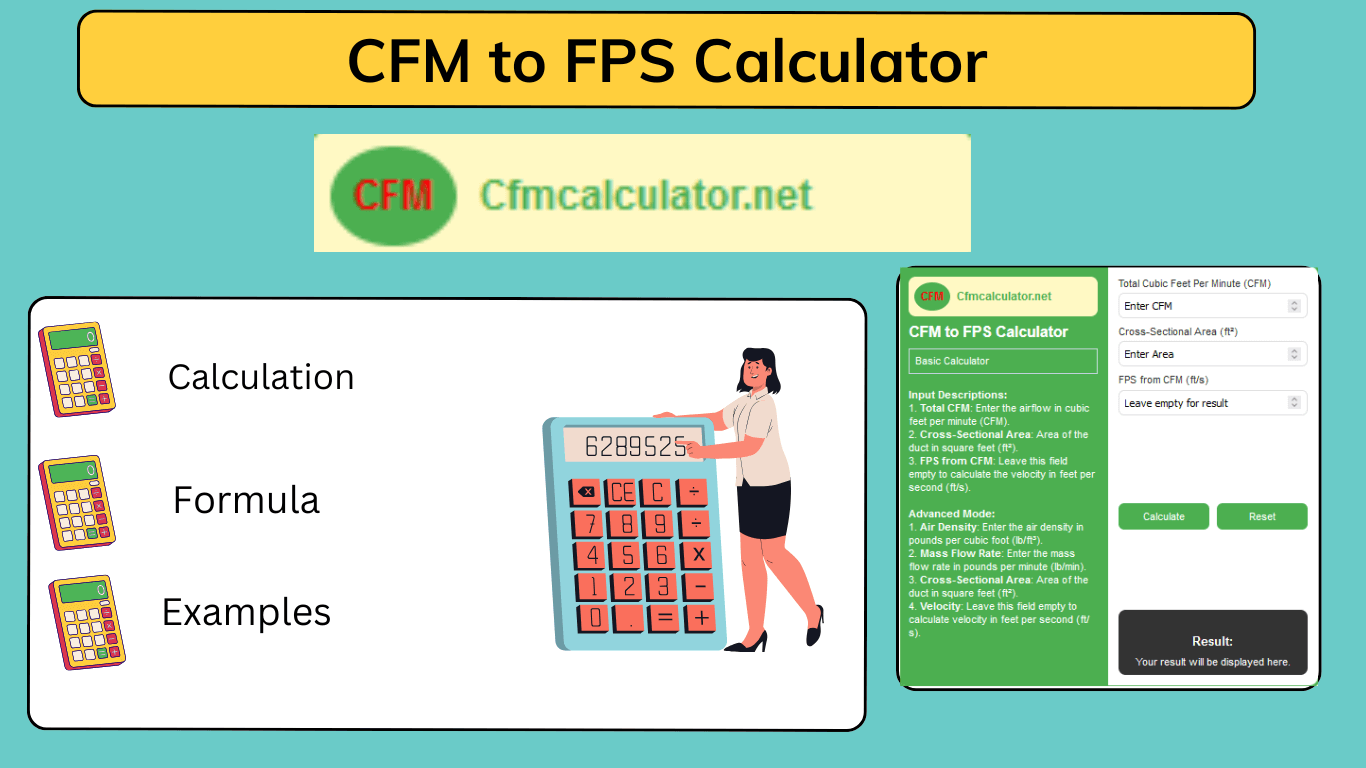
The CFM to FPS converter is a useful tool. You can easily determine feet per second (FPS) from cubic feet per minute (CFM), or to calculate CFM and cross-sectional area based on known inputs.
This calculator offer two mode for conversion. The basic mode is a simple tool for airflow calculation and advance tool provides more complex setups involving air density and mass flow rate.
Simply select the desired mode, enter the known values, and press “Calculate” for immediate results.
How to Calculate FPS from CFM
The basic formula to calculate air velocity (FPS) from CFM and cross-sectional area is:
Advance mode calculation involving air density and mass flow rate, the formula is:
Example
For example, you want to design a commercial HVAC system that needs to supply 5000 CFM of air through a 4 ft² duct. Use the formula, you can easily determine that the airflow velocity will be 20.83 FPS, It will ensure you that the duct size is appropriate to minimize air resistance and energy loss.
- CFM: 3000
- Cross-Sectional Area: 2.5 ft²
Basic Mode:
- Mass Flow Rate: 500 lb/min
- Air Density: 0.075 lb/ft³
- Cross-Sectional Area: 3 ft²
💡 Bonus Tip
Proper airflow velocity is most important in ventilation, exhaust systems, and for industrial airflow control. For more precise airflow analysis always use the advance mode for more.
Summary
| Mode | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Basic Mode | Converts CFM to FPS using cross-sectional area only |
| Advanced Mode | Uses air density and mass flow rate for detailed airflow calculations |
| Key Formula (Basic) | FPS = CFM ÷ (Area × 60) |
| Key Formula (Advanced) | FPS = Mass Flow Rate ÷ (Density × Area) |
| Best Use Cases | Ventilation planning, duct sizing, HVAC and industrial airflow setup |
FAQs
1. What does this calculator do?
It converts airflow (CFM) into velocity (FPS).
2. What values are needed?
CFM and area for basic mode; add density and mass flow for advanced mode.
3. Can I reverse the calculation?
Yes, you can also find CFM or area if FPS is known.
4. Who is this tool for?
HVAC pros, system designers, and industrial planners.
5. Why use advanced mode?
It gives more accurate results by factoring in air properties.