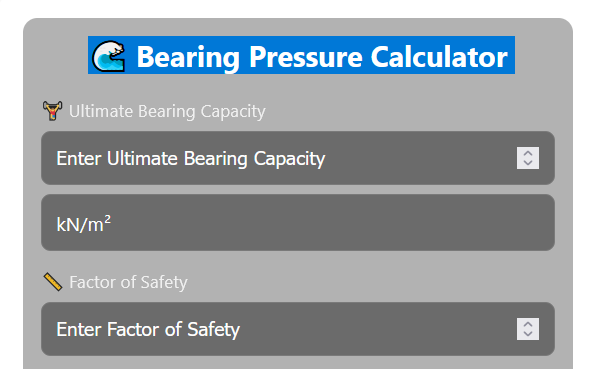
Bearing Pressure Calculator
Force applied to a surface per unit area is called bearing pressure. Engineers use it to make sure foundations and structures can handle heavy loads. Enter the bearing capacity and safety factor, and this tool will calculate the bearing pressure for you.
🌊 Bearing Pressure Calculator
Contents
This tool is useful for structural integrity, foundation design and for safety measurement.
I have given below step by step calculation example for kind information.
Why Engineers Needs To Calculate Pressure Of A Bearing
For example, consider an architectural firm building a ten-story office. The soil can handle up to 300 kN/m², but to keep things safe, engineers use a safety factor of 3.
By calculating an allowable bearing pressure of 100 kN/m², they can choose the right foundation—like a shallow one for strong soil or deep piles for weaker ground.
Formula To Calculate Bearing Pressure in Construction
Our calculator use following formula for calculation
Inputs:
- Ultimate Bearing Capacity (qᵤ): 300 kN/m²
- Factor of Safety (FS): 3
✅ The calculated allowable bearing pressure is 100 kN/m².
Final Line: Always check the soil before building to avoid foundation problems and sinking.
FAQs
1. What does this calculator compute?
It calculates allowable bearing pressure using ultimate bearing capacity and a safety factor.
2. Why is bearing pressure important?
It ensures that soil or foundation structures can support the applied loads safely.
3. What inputs are required?
Ultimate bearing capacity and the factor of safety.
4. What units can I use?
You can input values in kN/m², psi, or lb/ft².
5. Who should use this tool?
Engineers, architects, and construction professionals planning structural foundations.
Summary
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Ultimate Bearing Capacity (qᵤ) | The maximum pressure soil can withstand without failing. |
| Factor of Safety (FS) | A safety margin used to reduce risk and ensure stability. |
| Allowable Bearing Pressure (qₐ) | The final safe pressure to use in design: qₐ = qᵤ ÷ FS |
| Formula Used | qₐ = qᵤ / FS |
| Key Applications | Foundation design, site planning, and load distribution on soil or support. |